Fine Print: Understanding the Legal Gambling Landscape
- Category: Pics |
- 30 Aug, 2024 |
- Views: 443 |

The legal gambling landscape can be complex to navigate. With myriad regulations, license types, responsible gambling obligations, and taxes to consider, understanding the fine print is essential whether you're a business looking to enter the market or a casual bettor placing your first wager at Stake France. This guide breaks down key aspects of the legal gambling framework you need to know.
Obtaining a Gambling License
The cornerstone of operating legally as a gambling business or offering betting products and services is obtaining a valid gambling license from your jurisdiction. Gambling licenses generally fall into a few main categories:
Operator Licenses
Private companies looking to provide gambling platforms, software, websites, or other gaming and betting options to consumers must obtain an operator license. These allow you to offer games of chance and process payments and payouts. Operator licenses may be broad covering many verticals or narrower such as permitting only online sports betting.
Supplier Licenses
If you want to supply equipment like slot machines, betting terminals, or other gaming hardware including random number generators to licensed casinos, betting shops or online operators, you’ll need a gaming supplier license. You can learn more about slots here. These are issued to vendors who enable gambling operations but don’t directly interface with bettors.
Premises Licenses
Land-based venues and retail spaces such as casinos, bookmakers, bingo halls, racetracks, and arcades require a premises license to offer legal gambling to patrons onsite. This also applies to taverns, restaurants, truck stops and other locations housing video gaming terminals.
Key Employee Licenses
Operators must also ensure key employees like corporate officers, executives, risk managers, compliance leads, and finance personnel obtain individual key employee licenses. These certify the applicant meets character and fitness standards and undergoes background checks before taking jobs that could influence gambling operations.
Application Costs and Periodic License Renewal Fees
Applying for these various gambling operation, supplier, premises, and individual licenses involves upfront application fees that vary by jurisdiction but can cost from $500 into the tens of thousands. Applicants also pay background investigation costs. If approved, licenses must undergo renewal requiring additional fees every 1-5 years to continue operating legally.
Ongoing Compliance Standards and Reporting
Maintaining licenses after the initial application also involves adhering to strict regulatory standards like implementing responsible gambling programs, submitting to audits, maintaining transparency, and avoiding misleading advertising and promotions. Operators and suppliers additionally owe taxes and must submit frequent financial reports on performance and activities.
Understanding Gambling Taxes
Taxes represent a significant financial obligation tied to legal betting and gambling markets. The specific tax rates applied vary greatly depending on location and license type but often involve:
• Table Games Tax
• Slot or Video Lottery Terminal (VLT) Tax
• Sports Betting Tax
• Racetrack Betting Tax
• Bingo, Raffle, and Charitable Games Tax
Some jurisdictions levy a single tax rate on gross gaming revenue, which is all wagers minus payouts. Others apply specific tax rates per type of game. The average tax rate across the U.S. is 6.75% but ranges from over 30% in Pennsylvania to under 5% in Nevada.
Common Examples of Gambling Tax Rates
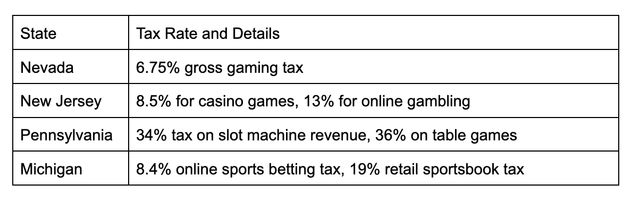
These taxes represent a significant expense but the specific rates tend to be clearly defined during the licensing application process.
Responsible Gambling and Player Protections
A key focus within legal and regulated gambling markets is responsible gambling initiatives and player protections. These include:
• Self-exclusion options: Players can voluntarily ban themselves from gambling sites and venues if they feel they have a problem.
• Deposit limits: Operators allow players to set caps on how much they can deposit which helps those struggling with addiction.
• Cool-off periods: Players can take a temporary break from gambling if they feel they are spending too much.
• Age verification: Strict ID checks ensure only adults over legal gambling age can participate.
• Problem gambling resources: Trained support staff help players identify issues while sites offer links to treatment and counseling services.
These measures aim to encourage healthy play and allow those struggling with compulsive gambling to access support.
By understanding the landscape around licenses, taxes, reporting obligations, and responsible gambling through this guide, players and businesses can better navigate the complex legal gambling industry. While dense regulations exist, they ultimately work to create a transparent, ethical gambling environment. Doing your due diligence in researching the requirements in your jurisdiction is key before participating in this regulated market.

